Snowflake
PRODFeature List
✓ Metadata
✓ Query Usage
✓ Data Profiler
✓ Data Quality
✓ Lineage
✓ Column-level Lineage
✓ dbt
✓ Stored Procedures
✓ Tags
✓ Sample Data
✓ Reverse Metadata (Collate Only)
✓ Auto-Classification
Iceberg Table Support: Collate supports ingestion and profiling of Iceberg tables through Snowflake. If your Iceberg tables are accessible via Snowflake, use this connector — it provides full metadata ingestion and profiler support for Iceberg tables without requiring a separate Iceberg connector.
- Requirements
- Metadata Ingestion
- Query Usage
- Data Profiler
- Data Quality
- Lineage
- dbt Integration
- Troubleshooting
- Reverse Metadata
Requirements
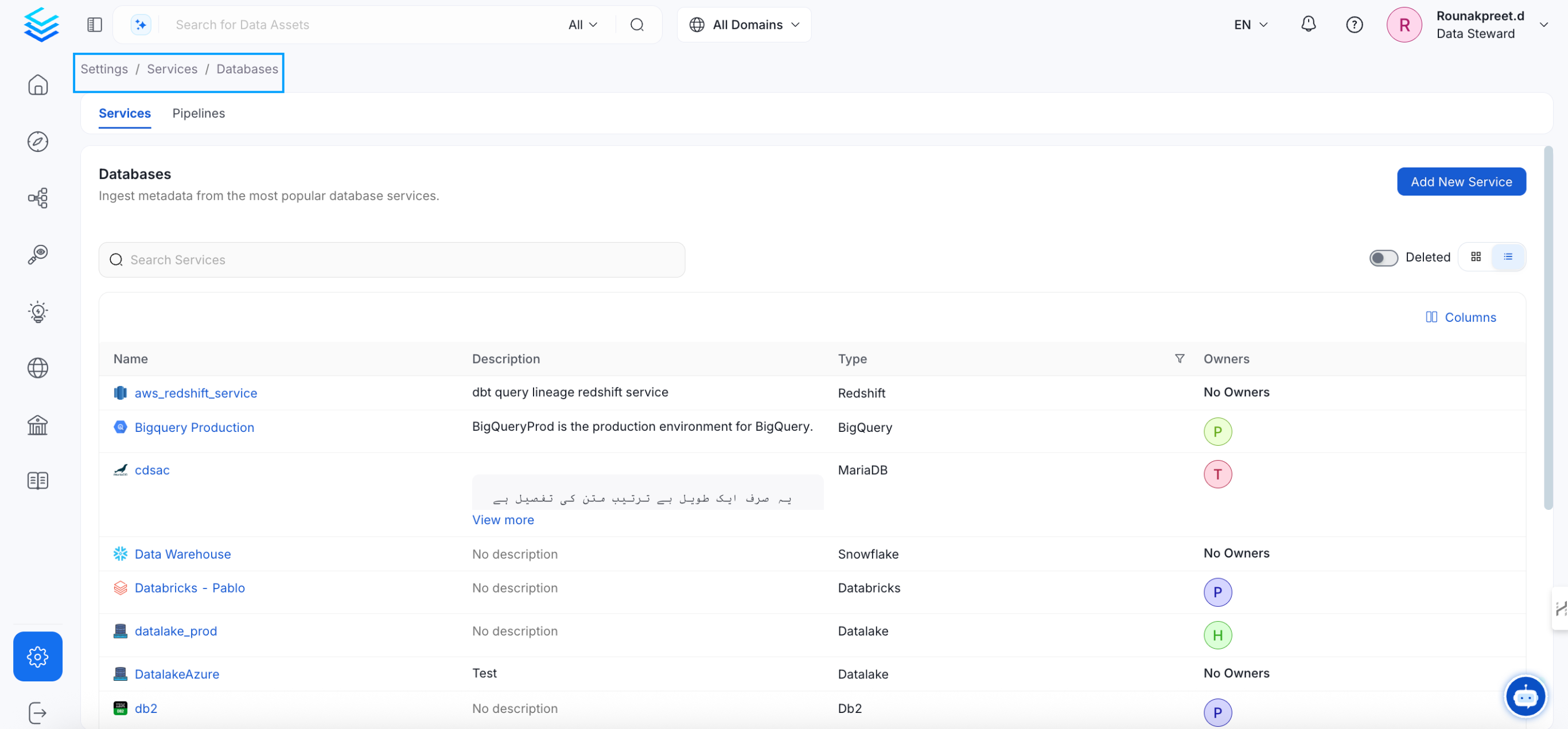
To ingest basic metadata snowflake user must have the following privileges:USAGEPrivilege on WarehouseUSAGEPrivilege on DatabaseUSAGEPrivilege on SchemaSELECTPrivilege on Tables
- Incremental Extraction: Openmetadata fetches the information by querying
snowflake.account_usage.tables. - Ingesting Tags: Openmetadata fetches the information by querying
snowflake.account_usage.tag_references. - Lineage & Usage Workflow: Openmetadata fetches the query logs by querying
snowflake.account_usage.query_historytable. For this the snowflake user should be granted theACCOUNTADMINrole or a role granted IMPORTED PRIVILEGES on the databaseSNOWFLAKE. You can find more information about theaccount_usageschema here. - Ingesting Stored Procedures: Openmetadata fetches the information by querying
snowflake.account_usage.procedures&snowflake.account_usage.functions.
Metadata Ingestion
Visit the Services Page
Click `Settings` in the side navigation bar and then `Services`. The first step is to ingest the metadata from your sources. To do that, you first need to create a Service connection first. This Service will be the bridge between OpenMetadata and your source system. Once a Service is created, it can be used to configure your ingestion workflows.

Name and Describe your Service
Provide a name and description for your Service.
Service Name
OpenMetadata uniquely identifies Services by their **Service Name**. Provide a name that distinguishes your deployment from other Services, including the other Snowflake Services that you might be ingesting metadata from. Note that when the name is set, it cannot be changed.
Connection Details
Connection Details
- Username: Specify the User to connect to Snowflake. It should have enough privileges to read all the metadata.
- Password: Password to connect to Snowflake.
- Account: Snowflake account identifier uniquely identifies a Snowflake account within your organization, as well as throughout the global network of Snowflake-supported cloud platforms and cloud regions. If the Snowflake URL is
https://xyz1234.us-east-1.gcp.snowflakecomputing.com, then the account isxyz1234.us-east-1.gcp. - Role (Optional): You can specify the role of user that you would like to ingest with, if no role is specified the default roles assigned to user will be selected.
- Warehouse: Snowflake warehouse is required for executing queries to fetch the metadata. Enter the name of warehouse against which you would like to execute these queries.
- Database (Optional): The database of the data source is an optional parameter, if you would like to restrict the metadata reading to a single database. If left blank, OpenMetadata ingestion attempts to scan all the databases.
- Private Key (Optional): If you have configured the key pair authentication for the given user you will have to pass the private key associated with the user in this field. You can checkout this doc to get more details about key-pair authentication.
- The multi-line key needs to be converted to one line with
\nfor line endings i.e.-----BEGIN ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY-----\nMII...\n...\n-----END ENCRYPTED PRIVATE KEY-----
- The multi-line key needs to be converted to one line with
- Snowflake Passphrase Key (Optional): If you have configured the encrypted key pair authentication for the given user you will have to pass the paraphrase associated with the private key in this field. You can checkout this doc to get more details about key-pair authentication.
- Include Temporary and Transient Tables:
Optional configuration for ingestion of
TRANSIENTandTEMPORARYtables, By default, it will skip theTRANSIENTandTEMPORARYtables. - Include Streams: Optional configuration for ingestion of streams, By default, it will skip the streams.
- Client Session Keep Alive: Optional Configuration to keep the session active in case the ingestion job runs for longer duration.
- Account Usage Schema Name: Full name of account usage schema, used in case your used do not have direct access to
SNOWFLAKE.ACCOUNT_USAGEschema. In such case you can replicate tablesQUERY_HISTORY,TAG_REFERENCES,PROCEDURES,FUNCTIONSto a custom schema let’s sayCUSTOM_DB.CUSTOM_SCHEMAand provide the same name in this field. When using this field make sure you have all these tables available within your custom schemaQUERY_HISTORY,TAG_REFERENCES,PROCEDURES,FUNCTIONS.
Advanced Configuration
Database Services have an Advanced Configuration section, where you can pass extra arguments to the connector
and, if needed, change the connection Scheme.This would only be required to handle advanced connectivity scenarios or customizations.
- Connection Options (Optional): Enter the details for any additional connection options that can be sent to database during the connection. These details must be added as Key-Value pairs.
-
Connection Arguments (Optional): Enter the details for any additional connection arguments such as security or protocol configs that can be sent during the connection. These details must be added as Key-Value pairs.

Test the Connection
Once the credentials have been added, click on Test Connection and Save the changes.

Configure Metadata Ingestion
In this step we will configure the metadata ingestion pipeline,
Please follow the instructions below



Metadata Ingestion Options
- Name: This field refers to the name of ingestion pipeline, you can customize the name or use the generated name.
-
Database Filter Pattern (Optional): Use to database filter patterns to control whether or not to include database as part of metadata ingestion.
- Include: Explicitly include databases by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Include field. OpenMetadata will include all databases with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other databases will be excluded.
- Exclude: Explicitly exclude databases by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Exclude field. OpenMetadata will exclude all databases with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other databases will be included.
-
Schema Filter Pattern (Optional): Use to schema filter patterns to control whether to include schemas as part of metadata ingestion.
- Include: Explicitly include schemas by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Include field. OpenMetadata will include all schemas with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other schemas will be excluded.
- Exclude: Explicitly exclude schemas by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Exclude field. OpenMetadata will exclude all schemas with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other schemas will be included.
-
Table Filter Pattern (Optional): Use to table filter patterns to control whether to include tables as part of metadata ingestion.
- Include: Explicitly include tables by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Include field. OpenMetadata will include all tables with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other tables will be excluded.
- Exclude: Explicitly exclude tables by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the Exclude field. OpenMetadata will exclude all tables with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other tables will be included.
- Enable Debug Log (toggle): Set the Enable Debug Log toggle to set the default log level to debug.
- Mark Deleted Tables (toggle): Set the Mark Deleted Tables toggle to flag tables as soft-deleted if they are not present anymore in the source system.
- Mark Deleted Tables from Filter Only (toggle): Set the Mark Deleted Tables from Filter Only toggle to flag tables as soft-deleted if they are not present anymore within the filtered schema or database only. This flag is useful when you have more than one ingestion pipelines. For example if you have a schema
- includeTables (toggle): Optional configuration to turn off fetching metadata for tables.
- includeViews (toggle): Set the Include views toggle to control whether to include views as part of metadata ingestion.
- includeTags (toggle): Set the ‘Include Tags’ toggle to control whether to include tags as part of metadata ingestion.
- includeOwners (toggle): Set the ‘Include Owners’ toggle to control whether to include owners to the ingested entity if the owner email matches with a user stored in the OM server as part of metadata ingestion. If the ingested entity already exists and has an owner, the owner will not be overwritten.
- includeStoredProcedures (toggle): Optional configuration to toggle the Stored Procedures ingestion.
- includeDDL (toggle): Optional configuration to toggle the DDL Statements ingestion.
- queryLogDuration (Optional): Configuration to tune how far we want to look back in query logs to process Stored Procedures results.
- queryParsingTimeoutLimit (Optional): Configuration to set the timeout for parsing the query in seconds.
- useFqnForFiltering (toggle): Regex will be applied on fully qualified name (e.g service_name.db_name.schema_name.table_name) instead of raw name (e.g. table_name).
-
Incremental (Beta): Use Incremental Metadata Extraction after the first execution. This is done by getting the changed tables instead of all of them. Only Available for BigQuery, Redshift and Snowflake
- Enabled: If
True, enables Metadata Extraction to be Incremental. - lookback Days: Number of days to search back for a successful pipeline run. The timestamp of the last found successful pipeline run will be used as a base to search for updated entities.
- Safety Margin Days: Number of days to add to the last successful pipeline run timestamp to search for updated entities.
- Enabled: If
- Threads (Beta): Use a Multithread approach for Metadata Extraction. You can define here the number of threads you would like to run concurrently.
Schedule the Ingestion and Deploy
Scheduling can be set up at an hourly, daily, weekly, or manual cadence. The
timezone is in UTC. Select a Start Date to schedule for ingestion. It is
optional to add an End Date.Review your configuration settings. If they match what you intended,
click Deploy to create the service and schedule metadata ingestion.If something doesn’t look right, click the Back button to return to the
appropriate step and change the settings as needed.After configuring the workflow, you can click on Deploy to create the
pipeline.

Incomplete Column Level for Views
For views with a tag or policy, you may see incorrect lineage, this can be because user may not have enough access to fetch those policies or tags. You need to grant the following privileges in order to fix it. checkout snowflake docs for further details.Reverse Metadata
Description Management
Snowflake supports full description updates at all levels:- Database level
- Schema level
- Table level
- Column level
Owner Management
❌ Owner management is not supported for Snowflake.Tag Management
Snowflake supports tag management at the following levels:- Schema level
- Table level
- Column level
Sensitive tag to a column in OpenMetadata, the corresponding masking policy will be automatically applied to that column in Snowflake.Owner Management
OpenMetadata does not support owner management for Snowflake, as Snowflake assigns ownership to roles rather than individual users. To work around this limitation, you can grant ownership to a specific role and then assign that role to the desired user.Custom SQL Template
Snowflake supports custom SQL templates for metadata changes. The template is interpreted using python f-strings.Here are examples of custom SQL queries for metadata changes:Requirements for Reverse Metadata
In addition to the basic ingestion requirements, for reverse metadata ingestion the user needs:ACCOUNTADMINrole or a role with similar privileges to modify descriptions and tags- Access to
snowflake.account_usage.tag_referencesfor tag management
Troubleshooting
Related
Usage Workflow
Learn more about how to configure the Usage Workflow to ingest Query information from the UI.
Lineage Workflow
Learn more about how to configure the Lineage from the UI.
Profiler Workflow
Learn more about how to configure the Data Profiler from the UI.
Data Quality Workflow
Learn more about how to configure the Data Quality tests from the UI.
dbt Integration
Learn more about how to ingest dbt models’ definitions and their lineage.