Kafka
PRODRequirements
Connecting to Kafka does not require any previous configuration. The ingestion of the Kafka topics’ schema is done separately by configuring the Schema Registry URL. However, only the Bootstrap Servers information is mandatory. Below are the required Permissions for fetching the Metadata:-- READ TOPIC
- DESCTIBE TOPIC
- READ CLUSTER
Metadata Ingestion
Visit the Services Page
Click `Settings` in the side navigation bar and then `Services`. The first step is to ingest the metadata from your sources. To do that, you first need to create a Service connection first. This Service will be the bridge between OpenMetadata and your source system. Once a Service is created, it can be used to configure your ingestion workflows.

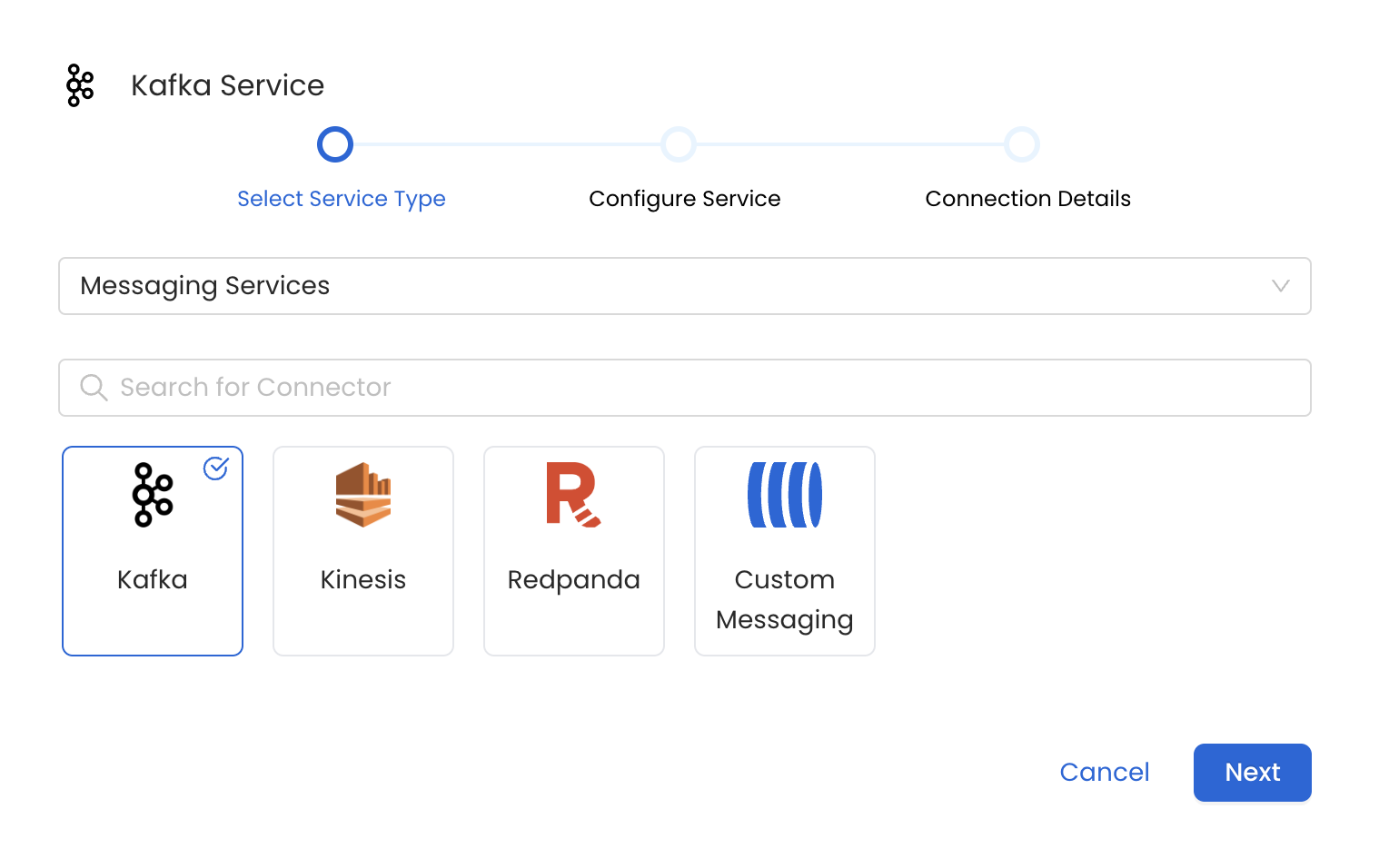
Name and Describe your Service
Provide a name and description for your Service.
Service Name
OpenMetadata uniquely identifies Services by their **Service Name**. Provide a name that distinguishes your deployment from other Services, including the other Kafka Services that you might be ingesting metadata from. Note that when the name is set, it cannot be changed.
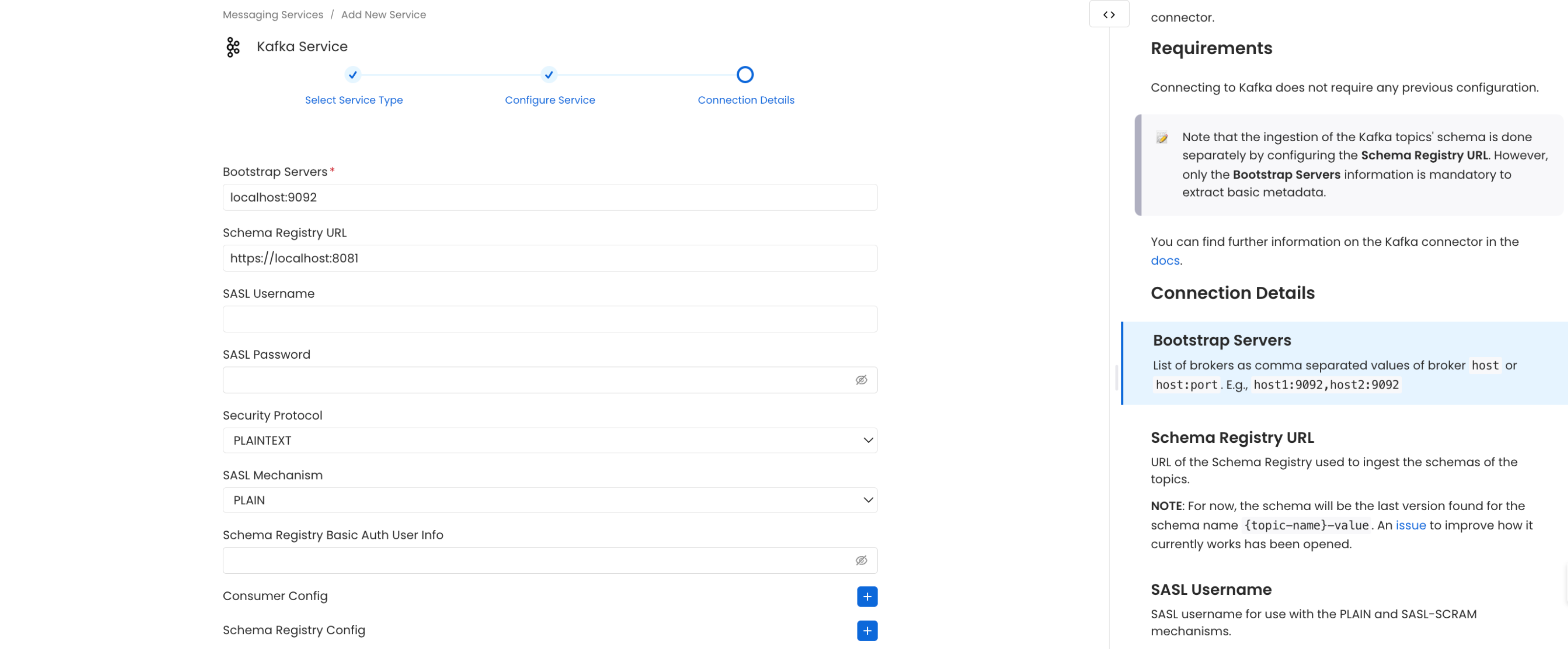
Connection Details
Connection Details
- Bootstrap Servers: List of brokers as comma separated values of broker
hostorhost:port. Example:host1:9092,host2:9092 - Schema Registry URL: URL of the Schema Registry used to ingest the schemas of the topics.
- SASL Username: SASL username for use with the PLAIN and SASL-SCRAM mechanisms.
- SASL Password: SASL password for use with the PLAIN and SASL-SCRAM mechanisms.
- SASL Mechanism: SASL mechanism to use for authentication.
- Basic Auth User Info: Schema Registry Client HTTP credentials in the form of
username:password. By default, user info is extracted from the URL if present. - Consumer Config: The accepted additional values for the consumer configuration can be found in the following link.
If you are using Confluent kafka and SSL encryption is enabled you need to add
security.protocolas key andSASL_SSLas value under Consumer Config - Schema Registry Config: The accepted additional values for the Schema Registry configuration can be found in the following link.
Test the Connection
Once the credentials have been added, click on Test Connection and Save the changes.

Configure Metadata Ingestion
In this step we will configure the metadata ingestion pipeline,
Please follow the instructions below

Metadata Ingestion Options
- Name: This field refers to the name of ingestion pipeline, you can customize the name or use the generated name.
- Topic Filter Pattern (Optional): Use it to control whether to include topics as part of metadata ingestion.
- Include: Explicitly include topics by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the ‘Include’ field. OpenMetadata will include all topics with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other topics will be excluded.
- Exclude: Explicitly exclude topics by adding a list of comma-separated regular expressions to the ‘Exclude’ field. OpenMetadata will exclude all topics with names matching one or more of the supplied regular expressions. All other topics will be included.
- Ingest Sample Data (toggle): Set the ‘Ingest Sample Data’ toggle to ingest sample data from the topics.
- Enable Debug Log (toggle): Set the ‘Enable Debug Log’ toggle to set the default log level to debug.
- Mark Deleted Topics (toggle): Set the ‘Mark Deleted Topics’ toggle to flag topics as soft-deleted if they are not present anymore in the source system.
Schedule the Ingestion and Deploy
Scheduling can be set up at an hourly, daily, weekly, or manual cadence. The
timezone is in UTC. Select a Start Date to schedule for ingestion. It is
optional to add an End Date.Review your configuration settings. If they match what you intended,
click Deploy to create the service and schedule metadata ingestion.If something doesn’t look right, click the Back button to return to the
appropriate step and change the settings as needed.After configuring the workflow, you can click on Deploy to create the
pipeline.

Securing Kafka Connection with SSL in OpenMetadata
To establish secure connections between OpenMetadata and Kafka, navigate to theAdvanced Config section. Here, you can provide the CA certificate used for SSL validation by specifying the caCertificate. Alternatively, if both client and server require mutual authentication, you’ll need to use all three parameters: ssl key, ssl cert, and caCertificate. In this case, ssl_cert is used for the client’s SSL certificate, ssl_key for the private key associated with the SSL certificate, and caCertificate for the CA certificate to validate the server’s certificate.